| Professor | |
| Name | Yau, Shueh-Lin |
| Phone: | (03)4227151 ext.65922 |
|
Professional field: Analytical Chemistry, Surface Chemistry, Electrochemistry |
|
| Research Interest | 1.Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Imaging of Well-Defined Electrified Interfaces 2.Electrocatalysis at Well-Ordered Noble Transition Metal Electrodes 3.Electrodeposition at Bare and Modified Metal Electrodes |
Diploma
| Country | School Name | Department | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|
Experience
| Duration |
|---|
| 2012.08 ~ 2015.07 |
| 2010.01 ~ Up to today |
| 2003.01 ~ Up to today |
| 1997.01 ~ 2003.01 |
| 1993.01 ~ 1997.01 |
| 1991.01 ~ 1993.01 |
Personal Honor
| Honor Category | Year | Award Name | Awarding Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inside School Honor | 2009 |
Personal Research
研究興趣
1.表面電化學
2.電子穿透顯微技術
Research
Research activities in my group have focused on using surface sensitive techniques such as scanning tunneling microscopy and surface enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy coupled with electrochemical methods to investigate electrified interfaces of metal single crystal electrodes, particularly platinum, gold, copper, palladium, rhodium etc. We have explored the electropolymerization of aniline, thiophene, pyrrole and their derivatives, the electrodeposition of copper, nickel, cobalt, and the electrocatalysis of Pt films or bulk electrodes toward electroxidation of CO, methanol, formic acid and toward oxygen reduction reaction - important electrochemical reactions occurring at the anode and cathode of fuel cells.
I. Electropolymerization of aniline
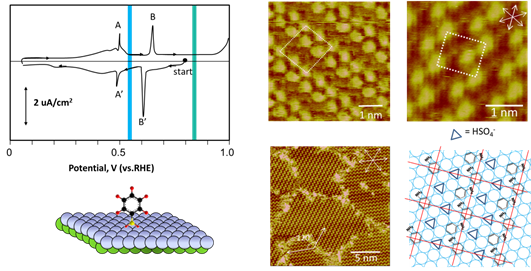
Adsorption of aniline molecules on Au(111) electrode
Cyclic voltammgram (below) obtained with Au(111) electrode in 0.1 M H2SO4 + 30 mM aniline shows two pairs of current spikes associated with the sudden transitions of aniline molecules adsorbed on the Au(111) electrode, which corresponds to the observation of two structures by STM. Aided by molecular-resolution STM imaging and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, we are able to determine the chemical compositions and dimensions of these spatial structures and finally propose a tangible model of aniline molecules adsorbed on the Au(111). These self-assembled aniline molecules are arranged in a head-to-tail orientation, which enabled molecular coupling into polyaniline molecules upon anodization at E > 0.9 V (vs. RHE).
Oxidative polymerization of aniline
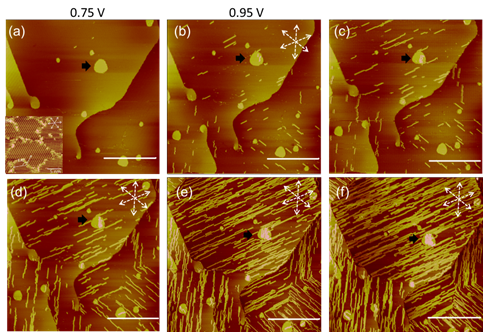
The followings are STM images collected as oxidation of aniline at E > 0.9 V (vs. reversible hydrogen electrode), producing linear segments aligned in the <110> direction on the Au(111) electrode. PAN grew to 50 nm long molecular wires. This anisotropic reaction was likely guided by specific molecular orientation of aniline and the nature of head-to-tail molecular coupling of polymerization.
II. Electrodeposition of Copper, Nickel and Cobalt
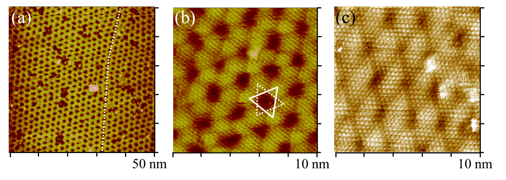
Electrodepsition has been important to metallize substrate, imparting uses to a number of industries. For example, Cu deposition has been an essential method to fabricate interconnects to silicon chips. Films of Ni and Co have intriguing magnetic properties, which are essential to fabricate hard drive for computers and switches. We have used STM to study the surface morphology and atomic structures of Ni and Co on gold and platinum electrodes. Shown below are STM images obtained with cobalt deposited on Pt(111) electrode in pH3 electrolyte containing chloride. Well-defined triangular textures suggest face-center close packed or hexagonal close packed atomic structures of the Co deposit. STM imaging also revealed Co film grew in layered manner and developed spiral defects as it thickened. Molecular resolution STM imaging was obtained to shed insight into the atomic structures of Co adatoms, which appear to form moire patterns, the typical structures observed with hetero-epitaxial deposition, as adatom and substrate have different lattice constants.
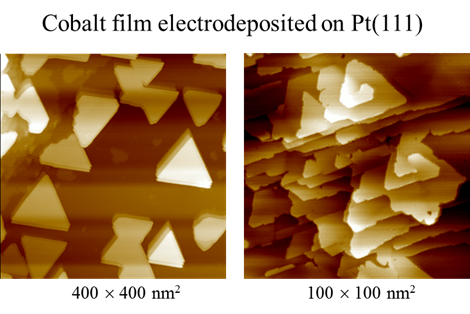
Atomic Structures of Cobalt film electrodeposited on Pt(111)
III. Electrocatalysis of Pt and its alloy films
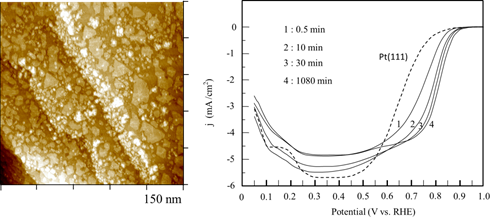
Platinum has been known to electrocatalyze methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions, two of the most relevant to the development of fuel cells used to power vehicle, electronic gadgets, and many. We have devised methods to prepare ultrathin films of Pt and its alloys and studied the electrocatalytic properties of these electrode materials. Shown below are a STM image of Pt thin film one atom thick on deposited Au(111) substrate, which was made by reduction of Pt salt by carbon monoxide. As CO was adsorbed on the Pt film, further Pt deposition into multilayer Pt was kinetically impeded. This Pt monolayer was used to performed oxygen reduction, as demonstrated by the current vs. potential profile obtained with a rotating Pt/Au(111) electrode. Results obtained with a few of these Pt/Au(111) electrodes made by different dosing times and with ordered Pt(111) electrode are shown (right). All Pt/Au(111) electrodes resulted in higher E1/2 potentials than that of Pt(111), attesting the advantage of these Pt films. This finding could be used to fabricate more practical electrodes for future fuel cell technology.
Personal Journal
2018, Electrified Interfaces of Pt(332) and Pt(997) in Acid Containing CO and KI: As Probed by In-situ Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, j. Phys. Chem. C
2017, Au(111)-Supported Pt Monolayer as the Most Active Electrocatalyst toward Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reactions in Sulfuric Acid, j. Phys. Chem. C
2016, Adsorption and Electrochemical Polymerization of Pyrrole on Au(100) Electrodes as Examined by In Situ Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, j. Phys. Chem. C
2015,Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Examination of Rubrene Deposited on Au(111) in Aqueous Solution ,j. phys. chem. c (SCI)
2014,In situ STM and ex situ XPS examination of the adsorption and polymerization of metanilic acid and aniline on Au(111) electrode ,j. electroanal. chem. (SCI)
2014,In situ scanning tunneling microscopy of the adsorption and polymerization of aniline on Au(1 1 1) electrode in nitric acid ,j. electroanal. chem. (SCI)
2014,Effects of Anions on the Electrodeposition of Cobalt on Pt(111) Electrode ,LANGMUIR (SCI)
2014,In Situ Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Imaging Self-Assembled Monolayers of Mercaptoacetic Acid and Cupric Ion on Au(111) Electrode ,j. electrochem. soc. (SCI)
2013,In situ scanning tunneling microscopy characterization of thienothiophene-based semiconducting organic molecules adsorbed on a Au(111) electrode ,surface science (SCI)
2013,In Situ Scanning Tunneling Microscopy of Electrodeposition of Indium on a Copper Thin Film Electrode Predeposited on Pt(111) Electrode ,Journal of Physical Chemistry C (SCI)
2013,Scanning Tunneling Microscopy of Superfilling in Formula Containing Chloride, Polyethylene Glycol and Bis-3-Sodiumsulfopropyl-Disulfide ,Journal of Electrochemical society (SCI)
2013,Use of 3,3-Thiobis(1-propanesulfonate) to Accelerate Microvia Filling by Copper Electroplating ,Journal of Electrochemical society (SCI)
2013,Potential-Induced Adsorption Behavior of Carboxyl-Terminated Alkanethiol on Au(111) Surfaces ,Journal of Physical Chemistry C (SCI)
2017, Au(111)-Supported Pt Monolayer as the Most Active Electrocatalyst toward Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reactions in Sulfuric Acid, j. Phys. Chem. C
2016, Adsorption and Electrochemical Polymerization of Pyrrole on Au(100) Electrodes as Examined by In Situ Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, j. Phys. Chem. C
2015,Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Examination of Rubrene Deposited on Au(111) in Aqueous Solution ,j. phys. chem. c (SCI)
2014,In situ STM and ex situ XPS examination of the adsorption and polymerization of metanilic acid and aniline on Au(111) electrode ,j. electroanal. chem. (SCI)
2014,In situ scanning tunneling microscopy of the adsorption and polymerization of aniline on Au(1 1 1) electrode in nitric acid ,j. electroanal. chem. (SCI)
2014,Effects of Anions on the Electrodeposition of Cobalt on Pt(111) Electrode ,LANGMUIR (SCI)
2014,In Situ Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Imaging Self-Assembled Monolayers of Mercaptoacetic Acid and Cupric Ion on Au(111) Electrode ,j. electrochem. soc. (SCI)
2013,In situ scanning tunneling microscopy characterization of thienothiophene-based semiconducting organic molecules adsorbed on a Au(111) electrode ,surface science (SCI)
2013,In Situ Scanning Tunneling Microscopy of Electrodeposition of Indium on a Copper Thin Film Electrode Predeposited on Pt(111) Electrode ,Journal of Physical Chemistry C (SCI)
2013,Scanning Tunneling Microscopy of Superfilling in Formula Containing Chloride, Polyethylene Glycol and Bis-3-Sodiumsulfopropyl-Disulfide ,Journal of Electrochemical society (SCI)
2013,Use of 3,3-Thiobis(1-propanesulfonate) to Accelerate Microvia Filling by Copper Electroplating ,Journal of Electrochemical society (SCI)
2013,Potential-Induced Adsorption Behavior of Carboxyl-Terminated Alkanethiol on Au(111) Surfaces ,Journal of Physical Chemistry C (SCI)
| Year |
|---|
| 2015 |
| 2014 |
| 2014 |
| 2014 |
| 2014 |
| 2014 |
| 2013 |
| 2013 |
| 2013 |
| 2013 |
| 2013 |
| 2013 |
| 2012 |
| 2012 |
| 2012 |
| 2012 |
| 2012 |
| 2012 |
| 2011 |
| 2011 |
| 2011 |
| 2011 |
| 2011 |
| 2010 |
| 2010 |
| 2010 |
| 2010 |
| 2010 |
| 2010 |
| 2010 |
| 2010 |
| 2009 |
| 2009 |
| 2009 |
| 2009 |
| 2009 |
| 2009 |
| 2009 |
| 2008 |
| 2008 |
| 2007 |
| 2007 |
| 2006 |
| 2006 |
| 2006 |
| 2005 |
| 2005 |
| 2005 |
| 2004 |
| 2004 |
| 2004 |